Specializing in Patellar Tendon Tear & Quadriceps Tendon Tear
Award-Winning Orthopedic Services in Orange County
About the Patellar Tendon Tear and Quadriceps Tendon Tear
If you are an athlete, especially when it comes to playing basketball or tennis, you rely on complex components of the knee to aid you in jumping, cutting, and sudden rapid movements. That is when the patellar tendons and quadriceps tendons serve a vital function.
The extensor mechanism is made up of the quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, patella, patellar tendon, and tibia. The main function of the patellar tendon and the quadriceps tendon is to straighten the knee and is essential for walking. The quadriceps tendon is the attachment of the quadriceps muscles to the patella (knee cap), and the patellar tendon is the attachment from the patella (knee cap) to the tibia (shin bone) (Figure 1).
The patellar tendon can be torn by a forceful contraction of the quadriceps while running, kicking or jumping. It can also be torn by falling directly on the kneecap. In both cases, the tear can be partial or completely ruptured (torn fully). A small tear can make it difficult to walk and perform other daily activities. A larger tear, however, can be quite disabling and usually requires surgery and physical therapy to regain full knee function.
The quadriceps tendon most often tears due to a sports injury, joint weakness or an underlying chronic knee condition. Injury typically arises when the knee is bent and under heavy load.
Symptoms of a Patellar Tendon Tear and Quadriceps Tendon Tear
Patellar tendon tears and quadriceps tendon tears occur when the quadriceps tendon contracts suddenly, with force exceeding the capacity of the tendons, often as a result of jumping during sport or falling on a flexed knee. A rupture (full tear) is commonly found in patients with pre-existing tendon degeneration / tendinosis.
Patients will develop acute pain around the knee cap often with an associated popping noise. The knee typically has significant swelling after rupture. Patients will have difficulty extending the knee and walking after the injury.
Diagnosis of Patellar Tendon Tears and Quadriceps Tendon Tears
A clinical exam is central to the diagnosis of patellar tendon and quadriceps tendon tear or rupture. A palpable gap is often felt at the respective tendon site. The surgeon will test the competence of the extensor mechanism by asking the patient to perform a straight leg raise against gravity; if the patient cannot extend the knee a significant tear is likely.
When the patellar tendon ruptures, the knee cap will be significantly elevated (patella alta) compared to the normal knee (Figure 2). While in quadriceps tendon ruptures, the knee cap will be slightly lower (patella baja).
Additional imaging studies are used to help confirm the diagnosis:
- X-rays can be helpful in determining the location of the extensor mechanism disruption.
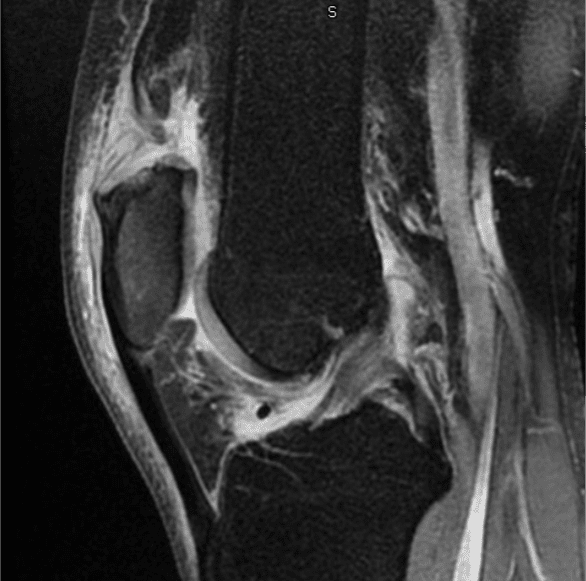
- MRI is often used to confirm diagnosis, and can help characterize tear pattern, underlying tendon disease, and any associated injuries (Figure 3).
Nonsurgical Treatment for Patellar Tendon Tears and Quadriceps Tendon Tears
Partial patellar and quadriceps tendon tears may be treated conservatively if patients continue to have the ability to extend the leg. Conservative treatment for a patellar tendon tear or a quadriceps tendon tear may include the following:
- Rest and modification/avoidance of activities that will aggravate your knee pain
- Applying ice to the affected area
- Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and swelling reduction (such as ibuprofen)
- Physical therapy to improve mobility, flexibility, and decrease pain
- Knee brace to rest the affected muscles and tendons
- Corticosteroid injections to relieve symptoms
Surgical Treatment for Patellar Tendon Rupture and Quadriceps Tendon Ruptures
Complete patellar tendon ruptures and complete quadriceps tendon ruptures require surgical intervention, because without repair, patients will be unable to extend the leg or support themselves when walking.
What to expect from Patellar Tendon Repair or Quadriceps Tendon Repair Surgery
- No weight-bearing or limited weight bearing on your injured leg for up to 4-6 weeks.
- Wearing a long brace or knee immobilizer that keeps your leg straight for 6 weeks.
- Limited ability to bend your knee for up to 12 weeks.
- No running for 12-14 weeks depending on leg strength.
- Return to sports at about 6 months depending on leg strength.
Figure 1: The Extensor Mechanism of the Knee
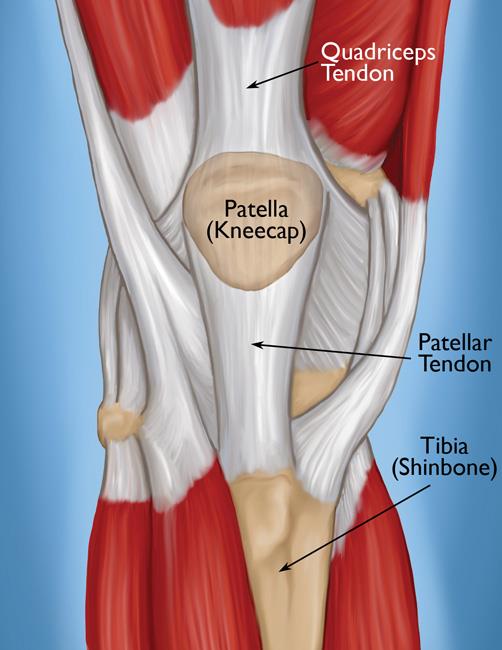
Figure 2: X-ray demonstrating patella alta due to patellar tendon rupture
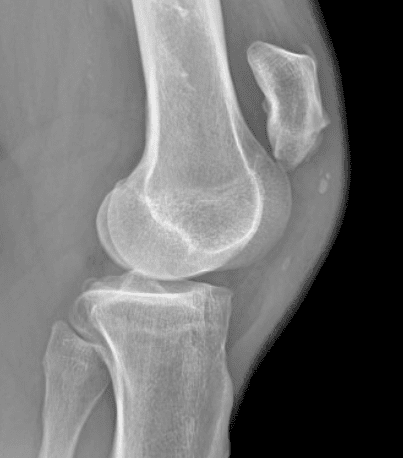
Figure 3: MRI of a quadriceps tendon rupture
Find a Knee Surgeon
If you have a patellar tendon tear or a quadriceps tendon tear or rupture our board certified, fellowship-trained knee surgeons will build a custom treatment plan to help you get back to doing the things you love doing.
Hoag Orthopedic Institute is ranked as one of the top Orthopedic Hospitals by U.S. News & World Report in 2022-2023. Contact Hoag Orthopedic Institute today to schedule a consultation with one of our knee doctors.
Find a knee surgeon that treats patellar tendon tears and quadriceps tendon tears. Call us at (949) 705-6493 to make an appointment.
-
 Returning to Boxing After Surgery Knee, Sports Medicine
Returning to Boxing After Surgery Knee, Sports Medicine"Procedure: Right Total Knee Arthroplasty When Brad retired nearly 20 years ago at age ..."
Read More -
 Back to Mobility and Me Knee
Back to Mobility and Me Knee"Procedure: Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty Seeing the world from the back of a Gold ..."
Read More -
 Back to Skiing Knee, Sports Medicine
Back to Skiing Knee, Sports Medicine"Procedure: Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty (SBTKA) – October 2016 ..."
Read More -
 Back to Gardening Knee
Back to Gardening Knee"Verna’s days are much more fruitful after having repairs to both knees. For the first ..."
Read More -
 Back to Golfing After Knee Replacement Knee
Back to Golfing After Knee Replacement Knee"Retired dentist Dr. Gregory Cramm and his wife, Cathy, enjoy going out for a nice ..."
Read More -
 Back to Racing Knee
Back to Racing Knee"Racecar driver Danny Thompson, 67, set the national land speed record at 406.7 mph in ..."
Read More -
 Back to Skiing and Snowboarding Knee
Back to Skiing and Snowboarding Knee"Rick Rengel, age 58, was having a great time speeding down a ski slope in Utah in ..."
Read More -
 Back to Cooking Knee
Back to Cooking Knee"“If I hadn’t had my knee replaced, I wouldn’t be out and about – I would be home in ..."
Read More -
 Back to a Family Christmas Knee
Back to a Family Christmas Knee"My wife, Lucille, was admitted to the Hoag Orthopedic Hospital, Irvine, California ..."
Read More -
 Back to the Golf Course Knee
Back to the Golf Course Knee"Shooting pain down the leg. Too painful to stand more than minutes. Sitting up to ..."
Read More













_20190109061103.png)